The People’s Republic of China, abbreviated as China, is situated in the east of Asia faces the Pacific Ocean in the sea, and borders on 14 countries, North Korea, Russia, Mongolia Kazakhstan, Kyrghyzstan, Kajikistan, Pakistan, Afghanistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Vietnam, Laos, and Burma.
China has a land area of about 9, 634,057 square kilometers, with a land coastline of 18,000 kilometers, and has thousands of islands including the South China Sea Islands. It is the third largest country, in term of land area. Its northernmost part is located on the central line of the main course of the Heilong River and north of the Mohe River in Heilongjiang Province; its southernmost tip is Zengmu Reef of the Nansha Islands of the South China Sea. The two sites are 5,500 km apart. Its easternmost part is at the confluence of the Heilong and Wusuli rivers; its westernmost tip is on the Pamirs in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. The span of the east and the west is 5,000 km (about 62 Latitudinal degrees). Taiwai island is the largest island, and Yangtze River is the longest river, and the Yellow River is the second longest river and also the mother river.
Its sea and land location is beneficial to China’s economy, trading with neighboring countries though land routes, and with other countries with marine routes. In the ancient China, there two famous trading roads, the Silk Road and Maritime Silk Road. In recent years, this two roads are restarted and China has made bountiful investment agreements with related countries which are beneficial to all parties. It is firmly believed that this restart will make great contributions to China’s trading with countries along the trading roads and to world economy.
In such a large territory, there are several kinds of climate, temperate continental climate, temperate monsoon and subtropical monsoon. Influenced by those climates, China, generally , is hot in summer and cold in winter, but specific temperature may be different in different regions. Spring and summer are rainy season, giving plenty rainfalls, which are an important source for China’s freshwater resources.
Full name: the People’s Republic of China
Capital city: Beijing
National flag: Five-star red flag, with a length and width proportion of 3:2
National anthem:
March of the Volunteers , composed by Tian Han
Lyrics: Arise, those who do not want to be slaves! We will use our flesh and blood to build another Great Wall. China has reached the brink of national collapse. All the people have been making their last outcry. Arise! Arise! Arise! All our hearts become one. Let us face the angry guns. March on! Let us face the angry guns. March on! March on! March on! On!
National day: October 1st . The People’s Republic of China was founded on September 21, 1949, with a celebration on October 1st, 1949, thus October 1st becomes the national day, and the seven-day national holiday starts from October 1st .
Population: 1.39 billions (2017). China has a permanent population of 1.39 billions in mainland, and has a urbanization rate of 58.52% in 2017. The population of old people at the age of 60 or above amounts to 0.24 billions, accounting for 17.3% of the total population, and population aging is a fact in China.
Calling code: 0086
Top legislature: National People’s Congress (NPC)
Location: In East Asia, by the western Pacific Ocean
Territory area: 9.6 million square km, third only to Russia and Canada.
Ethnic group: 56 ethnic groups are a common saying, in China has over 56 ethnic groups. The major groups are like Han nationality, Zhuang nationality, which have a big population, while some ethnic groups have a small population.
Main religions: Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism and Islam. Buddhism, Taoism and Confucianism are three local religions with thousands of years. Confucianism is the philosophy and wisdom, originated from the teaching of Confucius, a great philosopher and educator in China. The essence of Confucianism has influenced Chinese for a long time and it is one of the most popular religions. Taoism is one of oldest religions, and it values harmony, the harmony between human and nature.
Symbol: Great Wall, Forbidden City (Imperial Palace), dragon, phoenix, panda
Econmic center: Shanghai
Currency: Renmibin (RMB) yuan
Weights and measures: China applies the international weight measurement, with two units of g and kg. Still it also has a different traditional measure, with units of “gongjin”, “jin” and “liang”. one gongjin is equal to one kilogram, one jin, 500 g, and one liang, 50 g.
Languages
Chinese (Putonghua or Mandarin) is the official language of China, and it is also the most used language in the world. Chinese is based on northern dialects, and close to Beijing dialect, and it is the official language used in schools, and every Chinese learns it. In daily conversation, people may use dialects or Chinese, but in written course, only Putonghua is used.
In China, there are lots of dialects, and over eighty dialects can’t communicate with each other. Among decades of ethnic groups in China, most ethnic groups have their own dialects. Dialects usually have regional limits. Because of historical and geographical reasons, there are many dialects in the Chinese language, such at Wu, Guangdong and Fujian dialects.
Written Characters
The official written characters is Chinese (simple). In regions like Taiwan, Macau and Hongkong, people use traditional Chinese. Chinese and its written characters are in common use in China and also one of the five working languages designated by the United Nations.
The government has defined that the common speech of the Hah nationality is used as the common language. Chinese characters are used to record the Chinese language. Since the discovery of inscriptions on bones or tortoise shells of the Shang Dynasty (16th-11th century B.C.), the Chinese language has a history of about 6,000 years.
China has many languages and dialects, and most of the 55 ethnic groups in China have their own languages, about 30 of them have their own written languages, but some dialects are only the spoken ones, with no written letters. Some languages with written letters from minority nationalities are languages of the Zhuang, Man and Zang. Minority nationalities in China have the freedom to use and develop their own languages and written characters.
Time Zone
The official time zone of China is UTC+8. The land area of China is 6-degree Longitude from west to east. According to the demarcation of the world time zoning standard, the land area of China lies between the eastern fifth to ninth time zones. Currently, all the places in China have adopted the time accounting by the eastern eighth time zone for the sake of convenience. That is the commonly-known “Beijing Time”, and Beijing is in the eastern eighth time zone. But the transmission of Beijing Time is sent out from Pucheng, Shaanxi.
Chinese Traditional Festivals
China has quite a few major annual traditional festivals.
Spring Festival (Chinese Lunar New Year by Chinese lunar calendar):late January/mid-February. The spring festival is the most important festival, with a special meaning of family reunion. With the coming of this festival, there are two large “Tide of Return” migrations in China, one is before the festival, and another is after the festival. When the festival is on the corner, migrant workers return home to celebrate the holiday with their families.
The Lantern Festival: the fifth day of the first month of Chinese lunar calendar, just after Chinese New Year
Tomb-sweeping Day (Qingming Festival): it usually occurs from April 4th to 6th, and has three-day off. This festival is for the living to give thanks and express their miss to the dead. During the festival, people would go to sweep the tombs of their ancestors and offer sacrifices.
Dragon Boat Festival: 5th day of the 5th lunar month. The festival is celebrated for people’s respects paid to Qu Yuan, a great poet and patriot.
The Mid-autumn Day (Moon Cake Festival): 15th day of the 8th lunar month, usually Sep. or Oct.
The Double Ninth Festival (Chongyang Festival): 9th day of the 9th lunar month, usually in October
During festivals periods, hundreds of millions of migrant workers will return home and reunite with families, while millions of other Chinese would have a travel within the country. For this, every means of transportation would be quite crowded. Tickets of bus, train, and flight should be brought ahead of time. If you plan to have a trip in China on festival days, it may be necessary to book tour service or hotel well in advance.
Chinese Spring Festival
Administrative Divisions
The current administrative divisions of China are province, county (city) and township
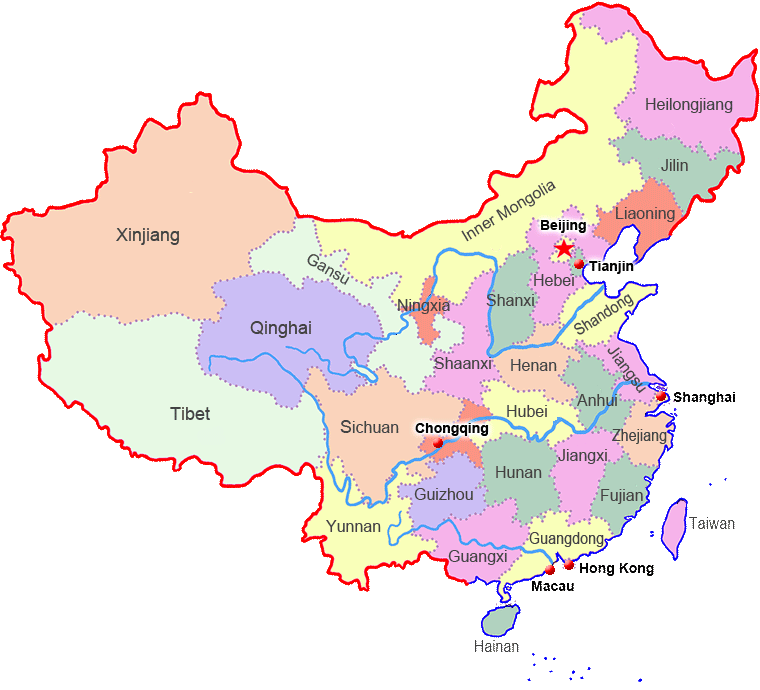
The country is divided into provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities directly under the central government, and special administrative regions. Provinces and autonomous regions are divided into autonomous prefectures, counties, autonomous counties, and cities; and Counties and autonomous counties are divided into townships, ethnic townships and towns. Autonomous regions, autonomous prefectures and autonomous counties are autonomous places of various ethnic groups. At present, China is divided into 23 provinces, five autonomous regions – each with a designated minority group, four municipalities directly under the central government and two special administrative regions ((SARs)), which enjoy a degree of political autonomy. Geographically, all 31 provincial divisions can be generally grouped into seven regions, including North China, East China, Northeast China, South China, Central China, Northwest China and Southwest China.
Twenty-three provinces includes: Hebei, Shanxi, Liaoning, Jiiin, Heilongjiang, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Shandong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Fujian, Taiwan, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Hainan
Five autonomous regions: Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Xinjiang, Guangxi, Tibet
Four municipalities: Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Chongging
Two special administrative regions: Hongkong, Macao
These 31 provincial-level divisions can be collectively referred to as “mainland China”, a term which usually excludes two SARs of Hong Kong and Macau.
Provincial Map of China
Resources
China boasts the most wildlife in the world and most of them are native to China and unique to the world, such as giant panda, snub-nosed golden monkey, and Chinese alligator; China’s dawn redwood and Cathaya argyrophylla are known as the living fossils of ancient plants.
Panda is one of the most precious animals, and it is regarded as national treasure in China. Sichuan is the living place for panda, and it has a research base for giant panda breeding. If you want to see panda, you may go to this research base, and you can see those cute pandas.
Wild animals: China has a great variety of wildlife, over 4,400 vertebrates, more than 100 rare species of the world: the giant panda, the golden monkey, the white-lipped deer, the South China Tiger, Crossoplilon mantchuricum, the white-flag dolphin, the Chinese alligator, and the crowned crane.
In Qinghai Lake, there are lots of wild birds, and during the period of bird migration, a spectacular scene is formed by thousands of birds and the lake, which attracts quite few tourist to watch. There are two periods of bird migration, May to April and October.
Plants: China has a great variety of plants, 32,000 species of higher plants, including nearly all the major kinds of vegetation found in the frigid and temperate zones of the northern hemisphere.
Popular flowers: Peony, azalea, primrose and felwort. Flowers like orchid, wintersweet, chrysanthemum, and lotus are loved by Chinese since the ancient time, because of their characters, and the first three flowers are highly praised by poets and writers.